Continuous Random Variable Example
The possible outcomes for this random experiment are S HH HT TH TT. If X is a random variable for the occurrence of the tail the possible values for X are 0 1 and 2.

Discrete Random Variable 11 Step By Step Examples
Example PageIndex1 Let the random variable X denote the time a person waits for an elevator to arrive.

. The annual rainfall in a. May be depth measurements at randomly chosen locations. X is the Random Variable The sum of the scores on the two dice.
Then X is a continuous rv. Implicit in the definition of a pmf is the assumption that it. Discrete Data can only take certain values such as 12345 Continuous Data can take any value within a range such as a persons height.
A random variable X is continuous if possible values comprise either a single interval on the number line or a union of disjoint intervals. First we implement this method for generating continuous random variables. Second the cdf of a random variable is defined for all real numbers unlike the pmf of a discrete random variable which we only define for the possible values of the random variable.
If X is a discrete random variable with discrete values x. It may be any set. With a discrete probability distribution each possible value of the discrete random variable can be associated with a non-zero probability.
Constructing a probability distribution for random variable Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to anyone anywhere. You could count from 0 seconds to a billion secondsa trillion secondsand so on forever. Difference between random variable and random process For example we can collect the random signal temperature Tt.
The uniform distribution is the simplest continuous random variable you can imagine. X is a value that X can take. Random Variables A random variable usually written X is a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenonThere are two types of random variables discrete and continuous.
A continuous distribution has a range of values that are infinite and therefore uncountable. Informally if we realize that probability for a continuous random. Hence we have four different types of random process.
In addition the type of random variable implies the particular method of finding a probability distribution function. For other types of continuous random variables the PDF is non-uniform. Probability distributions are either continuous probability distributions or discrete probability distributions.
Continuous Random Variables can be either Discrete or Continuous. A set of real numbers a set of vectors a set of arbitrary non-numerical values etcFor example the sample space of a coin flip would be. CDFs are also defined for continuous random variables see Chapter 4 in exactly the same way.
For example time is infinite. Mar 26 2016 Answer. Probability Distribution of a Continuous Random Variable.
In discrete time white noise is a discrete signal whose samples are regarded as a sequence of serially uncorrelated random variables with zero mean and finite variance. Khan Academy is a 501c3 nonprofit organization. If in the study of the ecology of a lake X the rv.
At the same time. Consider an example of tossing of two fair coins. Fig42 - PDF for a continuous random variable uniformly distributed over ab.
Throwing a dice is a purely random event. Discrete Random Variables A discrete random variable is one which may take on only a countable number of distinct values such as 01234. Notice the different uses of X and x.
A single realization of white noise is a random shockDepending on the context one may also require that the samples be independent and have identical probability distribution in other words independent and. A discrete random variable is a random variable whose values take only a finite number of values. A probability distribution is a mathematical description of the probabilities of events subsets of the sample spaceThe sample space often denoted by is the set of all possible outcomes of a random phenomenon being observed.
We know that the Probability Distribution Function PDF of the exponential distribution is. The range for X is the minimum. Suppose the longest one would need to wait for the elevator is 2 minutes so that the possible values of X in minutes are given by the interval 02.
A discrete random variable is a random variable that has countable values such as a list of non-negative integers. Suppose that we want to simulate a random variable X that follows the exponential distribution with mean λ ie. Thus a discrete probability distribution is often presented in tabular form.
Random processes can be discrete or continuous - meaning the outcome variable has a discrete or continuous range - and can occur in discrete or continuous time. The best example of a discrete variable is a dice.

Types Of Random Variables Discrete Continuous The Mighty By Dharmanath Patil Medium
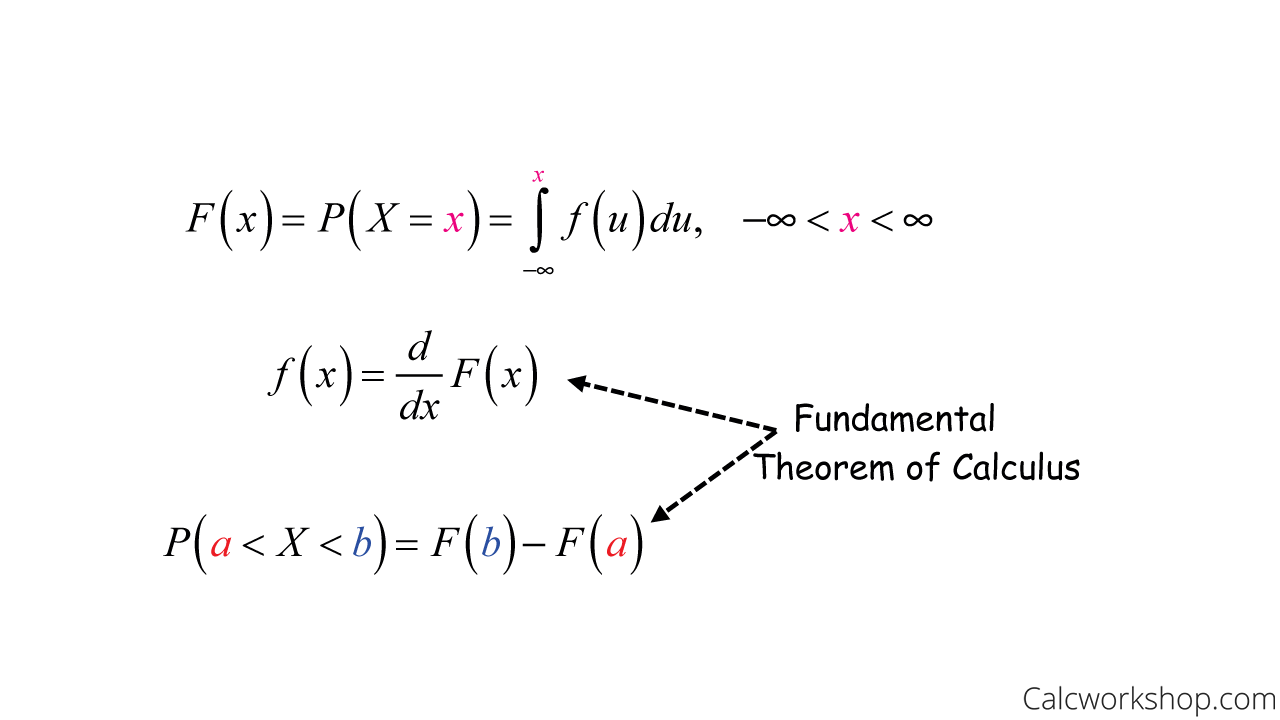
Continuous Random Variable Detailed W 7 Examples
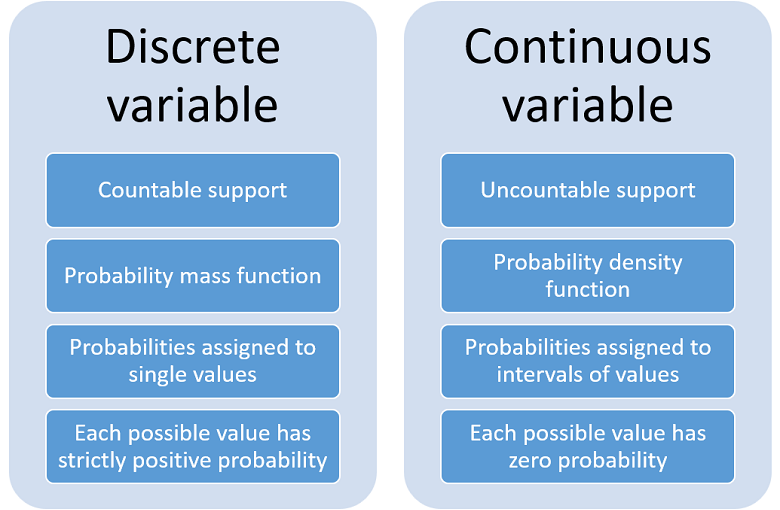
Continuous Random Variable Definition Examples Explanation

Continuous Random Variable Properties Probability Continuity Math Equations
0 Response to "Continuous Random Variable Example"
Post a Comment